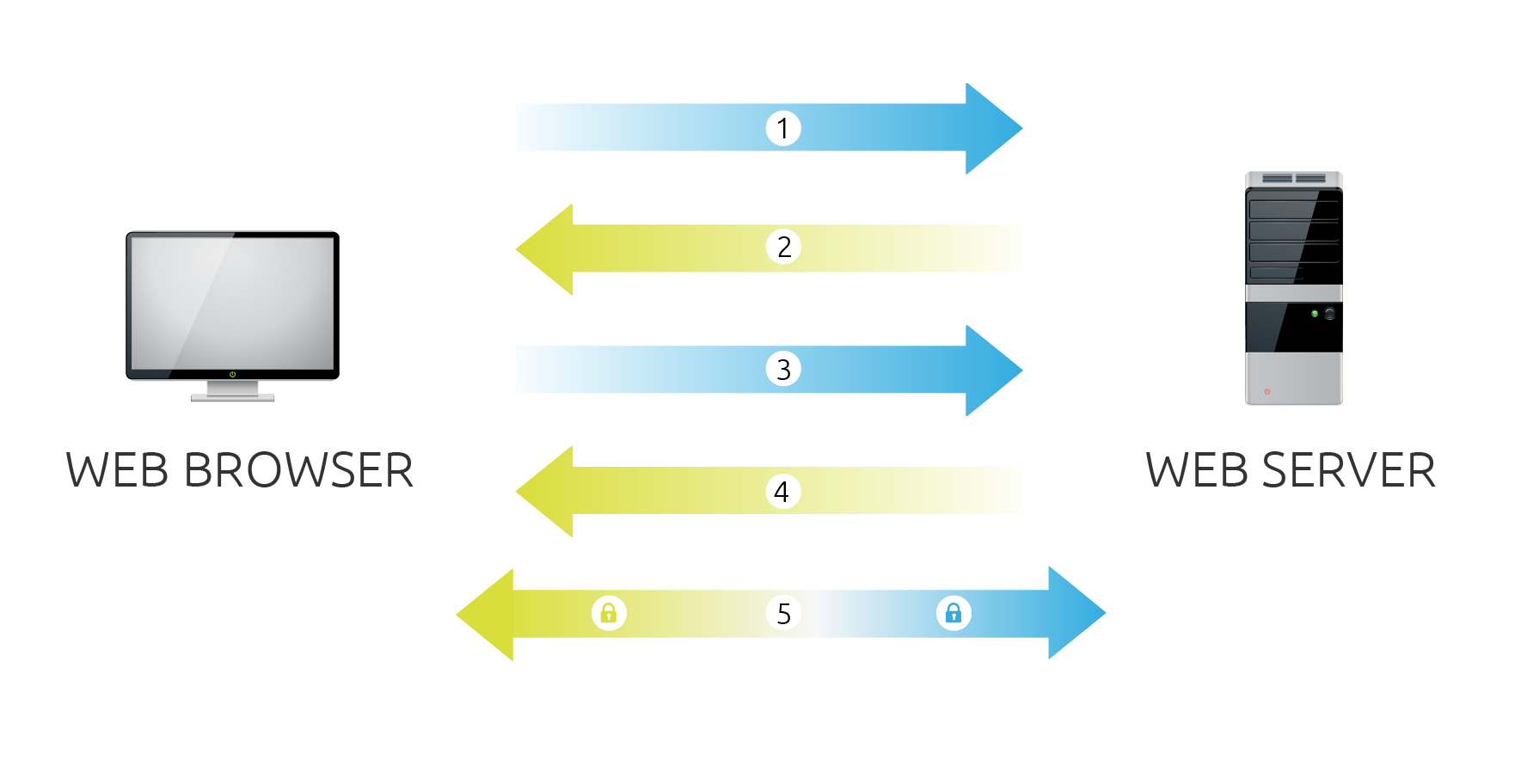
The following includs both the symmetric and asymmetric parts of the encryption, but also, for this section, you can focus on the role of the certificates and the Certificate Agency.
(Taken from https://www.digicert.com/ssl.htm)
I will bold the parts specifically about the certificate and Certificate Agency. (The rest is a good review of SSL.)

Wikipedia on Certification Authorities.
Webopedia on Certfication Authorites.
Extended Validation Digital Certificate - (Often refered to as "EV Digital Certificates)
JSR Note: For this Case Study, to be used just this year, I am not going to worry about copying and pasting. I'll just note from where it was done. In this case:
https://www.globalsign.com
As the highest ‘class’ of SSL available, Extended Validation SSL Certificates (EV SSL) activate both the padlock and the green address bar in all major browsers. EV SSL Certificates provide the strongest encryption level available and enable the organization behind a website to present its own verified identity to website visitors. EV SSL Certificates offer a stronger guarantee that the owner of the website passed a thorough, and globally standardized, identity verification process defined within the EV guidelines (a set of vetting principles and policies ratified by the CA/Browser forum). The Extended Validation identity verification process requires the applicant to prove exclusive rights to use a domain, confirm its legal, operational and physical existence, and prove the entity has authorized the issuance of the Certificate.
How can I recognize websites using EV SSL Certificates?A website using EV SSL Certificate will activate highly visible indicators directly on the browser address bar:
The green address bar, https:// and the padlock icon
The name of the Organization that owns the website and the name of the Certificate Authority that issued the EV SSL Certificate
![]()
Website with EV SSL Certificate on Chrome
![]()
Website with EV SSL Certificate on IE
![]()
Website with EV SSL Certificate on Safari
![]()
Website with EV SSL Certificate on Firefox
Certificate Agency -
Basically certificate agencies are organizations whose job it is to look into the trustworthiness of web sites who are seeking SSL status. They check their business record, to see if they have any criminal record, etc. So they offer a "stamp of approval" to a website, so that others can trust them.
For a general understanding of their role:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=SJJmoDZ3il8
Here are the main Certificate Agencies: You'll note that VeriSign is the biggest of these.

And this is from the actually not bad, overall, YouTube video:
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ffJKjX0dKvg